Normal penile discharge
Some of the penile discharges are normal to have, and every man can get it at some point: pre-ejaculate and smegma. [4] World Health Organization. Urethral discharge syndrome. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK572662/
Smegma
What is it?
It combines dead skin cells, oil from the sebaceous gland, and sweat. The normal amount of smegma keeps the area between the foreskin and penis head moist to decrease the friction. It can have healthy bacteria. But sometimes harmful bacteria overgrowth can happen. [11] Smegma https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/24281-smegma
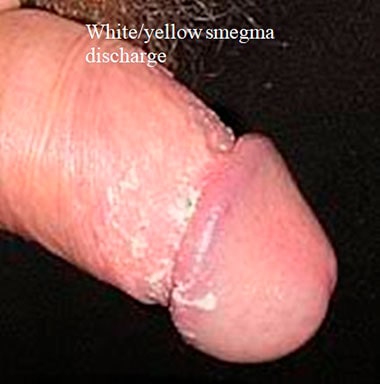
What is the discharge color and consistency?
It is a thick white or yellow substance. Does not cause any pain or smell.
What does smegma look like?
Pre-ejaculate
What is it?
Pre-ejaculate of pre-cum is the liquid produced by accessory sex glands (what is it?) The glands that are different from the prostate and testes: Cowper, Littre, and Morgagni. They open into the urethra at various places. during arousal. [12] What Is Pre-Ejaculate? https://www.webmd.com/men/what-is-pre-ejaculate
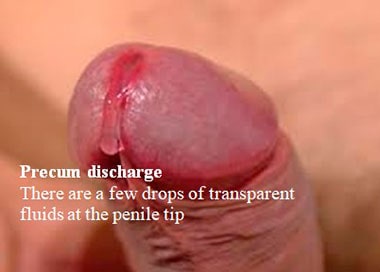
What is the discharge color and consistency?
The amount of precum differs for different people and depends on the intensity of the arousal. It can be from a few drops to 5 ml to the “feeling” of wetness. The fluid is usually clear and mucousy. What does precum look like?
Infectious penile discharge that is not an STD
These are the list of non-STD infections that can give penile discharge. However, other symptoms can also be present in addition to the discharge. Those additional symptoms usually help with differentiation.
Balanitis
What is it?
It is a male yeast infection that is more common in uncircumcised males. [10] Balanitis https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537143/
What is the discharge color and consistency?
The discharge color is white or yellow, often thick and lumpy, and can have an unpleasant smell.
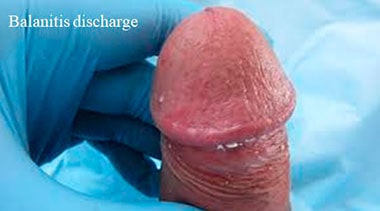
Additional symptoms help to differentiate it from other conditions
In addition to the discharge person usually have the head of the penis skin redness and swelling, itch and soreness, and even pain with urination
Prostatitis
What is it?
It is an infection of the prostate in men- a small gland located under the bladder. It can occur at any age. [5] Acute Bacterial Prostatitis: Diagnosis and Management https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2016/0115/p114.html
What is the discharge color and consistency?
Prostatitis discharge is minimal and white or yellow.When the condition is chronic,it might become blood-tinged and foul-smelling.
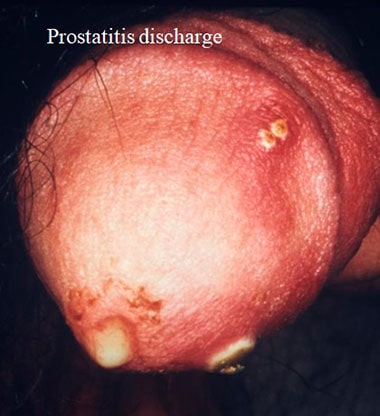
Additional symptoms help to differentiate it from other conditions.
Discharge is not the primary sign of prostatitis.
The most common signs are:
- The back, lower abdomen, penile, or testicular pain
- The urgency with urination and difficulty peeing
Non-STD urethritis
What is it?
Non-STD urethritis is also called non-specific urethritis or non-gonococcal urethritis. It is the infection of the urethra (tube inside the penis) that is caused by diseases other than chlamydia or gonorrhea. It can be caused by ureaplasma, mycoplasma, trichomoniasis, or other infections.
What is the discharge color and consistency?
The discharge is usually scanty, mucoid, or watery consistency. The color of the discharge is white or clear.
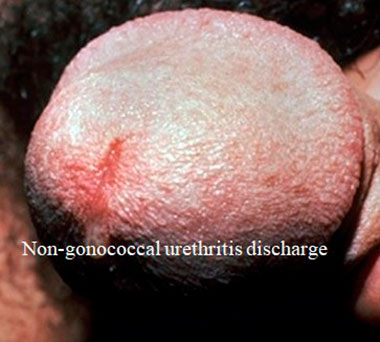
Additional symptoms help to differentiate it from other conditions.
In addition to the main symptoms of penile discharge the non-gonococcal urethritis can cause:
Pain with urination increased urinary frequency and itch inside the urethra
UTI or bladder infection
What is it?
It is a urinary bladder infection caused by skin or rectal bacteria entering the bladder. Unlike females, it is less common in males.
What is the discharge color and consistency?
Even though the discharge is uncommon, it is scanty and milky white or yellow when it happens.
Additional symptoms help to differentiate it from other conditions.
The main symptoms of bladder infections are:
- Burning, increased frequency, and urgency with urination
- Cloudy and foul-smelling urine
- Urine that contains blood.

STD penile discharge
The most common thing that can give penile discharge for sexually active men is STD-related discharge
So, the following STDs can cause penile discharge:
Chlamydia
What is it?
Chlamydia is one of the most common STDs. Only 15% of males infected with chlamydia get urethral discharge. [1] About chlamydia https://www.cdc.gov/chlamydia/about/index.html
What is the discharge color and consistency?
Chlamydia discharge is scanty, thin, or watery consistency. It is usually white, yellow, or colorless.
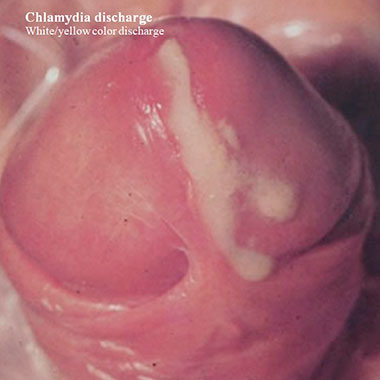
Additional symptoms help to differentiate it from other conditions.
The most common symptom of chlamydia in males is pain with urination -25 % of males infected with chlamydia get it.
Other symptoms might include redness at the tips of the penis and swollen local lymph nodes.
Gonorrhea
What is it?
Gonorrhea is another common STD that can cause penile discharge. It is caused by the bacteria Neisseria Gonorrhea. [2] About gonorrhea https://www.cdc.gov/gonorrhea/about/index.html
What is the discharge color and consistency?
Gonorrhea discharge is usually abundant and thick (creamy). It is typically green or yellow.
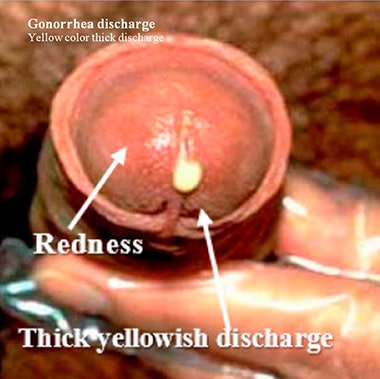
Additional symptoms help to differentiate it from other conditions.
Urinary symptoms of burning, urgency, and increased frequency of urination are common. Testicular pain is possible in advanced cases.
Trichomoniasis
What is it?
It is another common STD. It is caused by a parasite called Trichomonas vaginalis. [9] Trichomoniasis https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK534826/
What is the discharge color and consistency?
Trichomonas penile discharge is not very common. It is usually very insignificant, thin, colorless, or white when it happens.
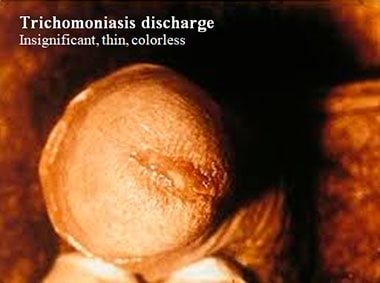
Additional symptoms help to differentiate it from other conditions.
The most common symptoms of trichomoniasis in males are:
- Itch and irritation of the penile tip
- Mild burning with urination and ejaculation.
Mycoplasma
What is it?
Mycoplasma Genitalium or Mycoplasma Hominis (less frequently) can cause penile discharge. [6] What is Mycoplasma Genitalium? https://www.devonsexualhealth.nhs.uk/stis/mycoplasma-genitalium/
What is the discharge color and consistency?
The mycoplasma penile discharge is infrequent and straightforward or pus-like.
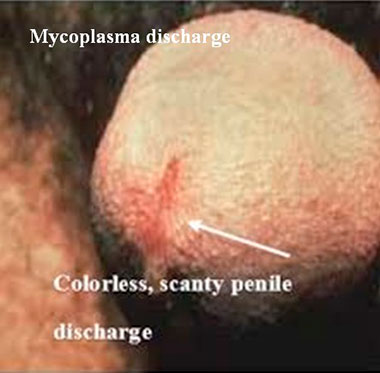
Additional symptoms help to differentiate it from other conditions.
The most common symptoms of mycoplasma infection are mild penile burning with urination and itch inside the urethra.
Ureaplasma
What is it?
Ureaplasma is not considered a classic sexually transmitted infection (STI), but it can be passed through sex. It can be naturally present in the sexually active female vagina without causing any disease. The overgrowth of the bacteria can cause irritation and discharge. [8] Ureaplasma and BPD https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3628630/
What is the discharge color and consistency?
Penile discharge is very uncommon. It is very minimal, thin, and colorless.
Additional symptoms help to differentiate it from other conditions.
The most common ureaplasma symptom in males is burning with urination.
When to see a doctor?
Any penile discharge that is clear and a result of sexual arousal before and right after sex is typical.
But for any discolored discharge: grey, yellow, green, bloody, or cheesy, the doctor should be seen.
Another reason for seeing the doctor is additional symptoms such as urinary symptoms (burning, increased urgency, and frequency with urination), testicular pain, rash, or fever and chills.
Diagnosing penile discharge
Most of the time, penile discharge suggests an infection, so establishing a diagnosis is necessary.
There are several ways of establishing the diagnosis:
Physical exam.
With a physical exam, the doctor can make a presumptive diagnosis and start the treatment.
Testing
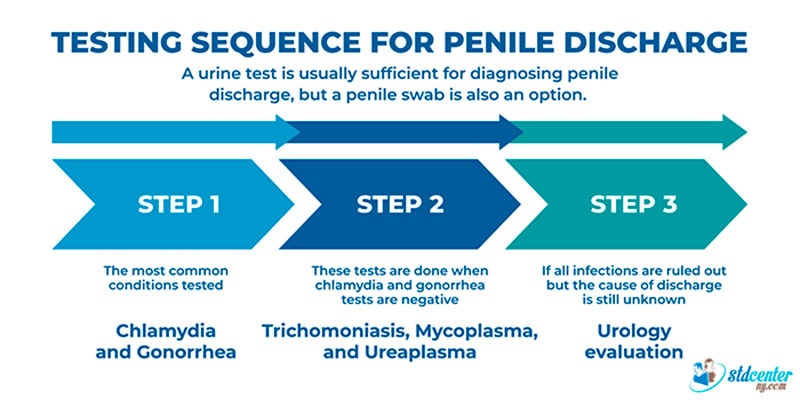
Testing is the ultimate way to determine the diagnosis. A urine test is usually sufficient for diagnosing penile discharge, but a penile swab is also an option.
Most commonly, the testing is done in three steps:
- Most common infections-chlamydia and gonorrhea- tested first.
- If common infections are undetected, further testing for trichomoniasis, mycoplasma, and ureaplasma is necessary.
- If all infections are ruled out but the cause of discharge is still unknown, the urological specialist evaluation is necessary.
Treating penile discharge
Penile discharge is usually caused by infection-Chlamydia, Gonorrhea, Trichomoniasis, Prostatitis, UTI, Mycoplasma, and Ureaplasma- which is why antibiotics are often used.
Improving hygiene (warm water wash once a day) is advised when the discharge is non-infectious-smegma and the initial stage of balanitis.
Treatment, depending on the cause, ranges from one-time medication (for Gonorrhea) to a maximum of one(Chlamydia) to two weeks (Mycoplasma).
One week after completing the treatment, sexual activity can be resumed.
Complications
There are a wide range of complications from untreated penile discharge:
- Epididymitis (infection of the tube carrying sperm from the testicle) [3] NHS. Gonorrhea: complications. https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/gonorrhoea/complications/
- Orchitis (testicular infection)
- Kidney infection
- Sepsis (when the body’s immune system overreacts to infection)
Source
-
About chlamydia
https://www.cdc.gov/chlamydia/about/index.html -
About gonorrhea
https://www.cdc.gov/gonorrhea/about/index.html -
NHS. Gonorrhea: complications.
https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/gonorrhoea/complications/ -
World Health Organization. Urethral discharge syndrome.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK572662/ -
Acute Bacterial Prostatitis: Diagnosis and Management
https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2016/0115/p114.html -
What is Mycoplasma Genitalium?
https://www.devonsexualhealth.nhs.uk/stis/mycoplasma-genitalium/ -
Diseases Characterized by Urethritis and Cervicitis
https://www.cdc.gov/std/treatment-guidelines/urethritis-and-cervicitis.htm -
Ureaplasma and BPD
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3628630/ -
Trichomoniasis
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK534826/ -
Balanitis
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537143/ -
Smegma
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/24281-smegma -
What Is Pre-Ejaculate?
https://www.webmd.com/men/what-is-pre-ejaculate